Surface Treatment of Metals and Plastics (STM)
A surface treatment is a process applied to the surface of a material to make it better in some way, for example by making it more resistant to corrosion or wear. Surface treatment of metals dates back to ancient Egyptians using gold decoratively. Gold and silver plating was well-known by the 13th century AD.
In general, surface treatment is employed to alter or enhance the mechanical, electrochemical, and/or thermal performance of a material. The technique used largely depends on material application as well as the desired property.
In this blog, we take a cursory look at one of the most commonly applied techniques in surface treatment of metals and plastics in electronics contract manufacturing: Electro-Plating.
Electro-Plating Basics
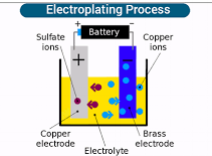
Simply put, electro-plating is a process that uses electric current to dissolve a superior metal like chrome, zinc, or gold, so that they form a thin metal coating on the workpiece, which is either a metal or a plastic piece.
It is done by immersing the workpiece and a bar of the superior metal in a solution containing the metal ions. The superior metal is connected to the anode (positive) of the power supply. The cathode (negative) is the workpiece, the substrate to be plated. The power supply is regulated to minimize ripples and to deliver a steady current. As the current is applied, the superior metal is dissolved in the solution and “plates out” on the workpiece, forming a thin but durable coating of metal. Sometimes the process repeats so multiple coatings can be placed onto the workpiece.
Oftentimes, additional chemicals are added to make the deposit bright and shiny. Without these chemicals, the metal deposit would look dull. For example, in today’s auto industry, various car parts are originally manufactured by steel, and are plated with several layers of nickel for corrosion protection, followed by a layer of chrome for decorative purposes.
Benefits Of Electro-Plating:
- Improved Corrosion Resistance– It is widely recognized that nickel and chromium plating improve corrosion resistance.
- Improve Hardness - Certain automobile parts may tarnish over time. Plating helps prevent this, prolonging the time that the vehicle looks new and attractive.
- Plastic Part Metallization – Plastics, which are cheaply available and easily molded or formed, have distinctive properties such as insulation and flexibility. Electro-plating can make plastic parts electrically conductive, while simultaneously improving their appearance. This improves the durability of plastic components and achieves a high value, metal-like appearance similar to gold, brass, and chromium.
- Performance Enhancement – Including applications requiring thermal protection or electrical conductivity, usually in selected areas.
- Improved Aesthetics - Electro-plating allows designers to create plastic products which have the ability to create very unique shape that is functional and aesthetically appealing.
- Extend the life of metals and plastics or reduces consumption of other raw materials. For example, electro-plating of precision fuel injectors for automotive engines to reduce fuel consumption.
Commercial Applications:
Owing to its many benefits the surface treatment of metals and plastics it is therefore largely a service to many industries as below:
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Home appliances
- Telecommunications equipment
- Heavy engineering products
- Construction hardware
- Medical devices
Need help finding an outsourcing manufacturing partner?
Send our experts a message so we can help.
Enjoyed this article? Don't forget to share.